Basic stance
The Kyorin Group’s Charter of Corporate Conduct details our understanding that “the tackling of environmental issues is a mission for all humankind and an imperative component of the very existence of corporations to which it remains voluntarily committed.” Business activities that take into account climate change and other environmental considerations are one example of our materiality.
Following our basic policy our stainability, the Group promotes reduced use of the environmentally harmful materials and the effective use of the world’s limited resources through energy and resource conservation, waste reduction, and enhanced chemical substance management in all our business activities. By setting and constantly reviewing objectives and targets for these initiatives, we are voluntarily and proactively committed to protecting the environment and preventing pollution.
Information disclosure based on TCFD recommendations
We have endorsed the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Following those recommendations, we have identified climate-related risks and opportunities and are addressing climate change and other environmental issues.
Governance
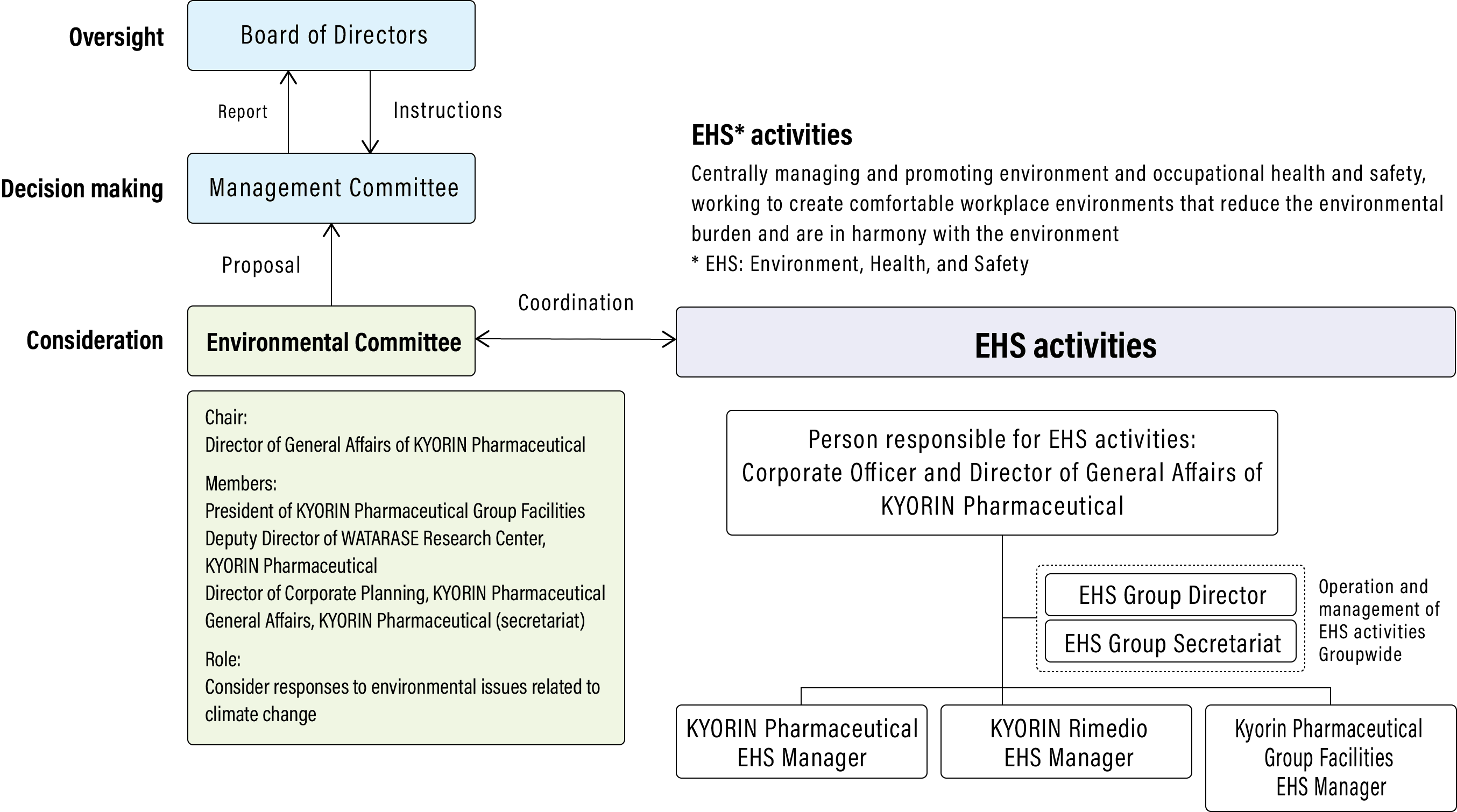
The Group has established an Environmental Committee, chaired by the corporate officer in charge, to implement and promote environmental measures, including ones addressing climate change, as a structure to consider environmental measures at the Group level.
Led by General Affairs, the committee is primarily composed of directors, corporate auditors, and corporate officers responsible for plants and research centers doing business related to the environment in local communities or involved in management strategies. It considers responses to environmental issues (vision, targets, road maps, etc.), then reviews them.
In coordination with environmental, health, and safety (EHS) activities, the committee identifies and evaluates risks and opportunities related to climate change and comprehensively compiles additional measures that it proposes to the Management Committee, with the resulting decisions reported to the Board of Directors.
Strategy
Regarding environmental issues, we are pursuing the challenge of “carbon neutrality by 2050” as part of our long-term vision. We are considering a gradual transition and new capital investments in energy from renewable sources to reduce CO2 emissions, with a target of “reducing CO2 emissions 46% from the fiscal 2015 level by fiscal 2030.”
We are promoting the effective use of the world’s limited resources and have set targets to protect the environment under the important themes of preventing global warming, protecting resources, and living in harmony with the natural environment.
All Group plants have obtained ISO 14001 certification, an international standard for environmental management systems. We will maintain and continue these measures going forward.
Risk management
The effects on the Kyorin Group’s business and management from global warming and climate change themselves, as well as changes to the business environment from long-term policy related to climate change, are broken down as physical risks and earnings opportunities caused by climate change and transition risks to a decarbonized society, and undergo a scenario analysis.
The scenario analysis is carried out by referencing documents and materials including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (the IPCC’s) Sixth Assessment Report’s SSP 1-1.9 (1.5˚C scenario) and SSP 5-8.5 (4˚C scenario).
1.5℃ Scenario
| Segment | Event | Risks | Response policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policies, laws and regulations | Introduction of an environmental (carbon) tax |
|
|
| Installation of equipment and machinery |
|
|
|
| Market | Changes in procurement/ operational costs |
|
|
| Evaluation | Assessment from investors |
|
|
4℃ Scenario
| Segment | Event | Risks | Response policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute risk | Direct damage from unusual weather (typhoons, heavy rains, etc.) |
|
|
| Chronic risk | Changes in location of centers, procurement, and operations from changes in climate patterns, higher temperatures, rising sea levels, etc. |
|
|
| Segment | Event | Earnings opportunity | Response policy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market changes | Changes in disease trends |
|
|
Indicators and targets
Tackling environmental issues is a mission for all humankind. We are voluntarily pursuing the challenge of “carbon neutrality by 2050” as an imperative component for the very existence of corporations.
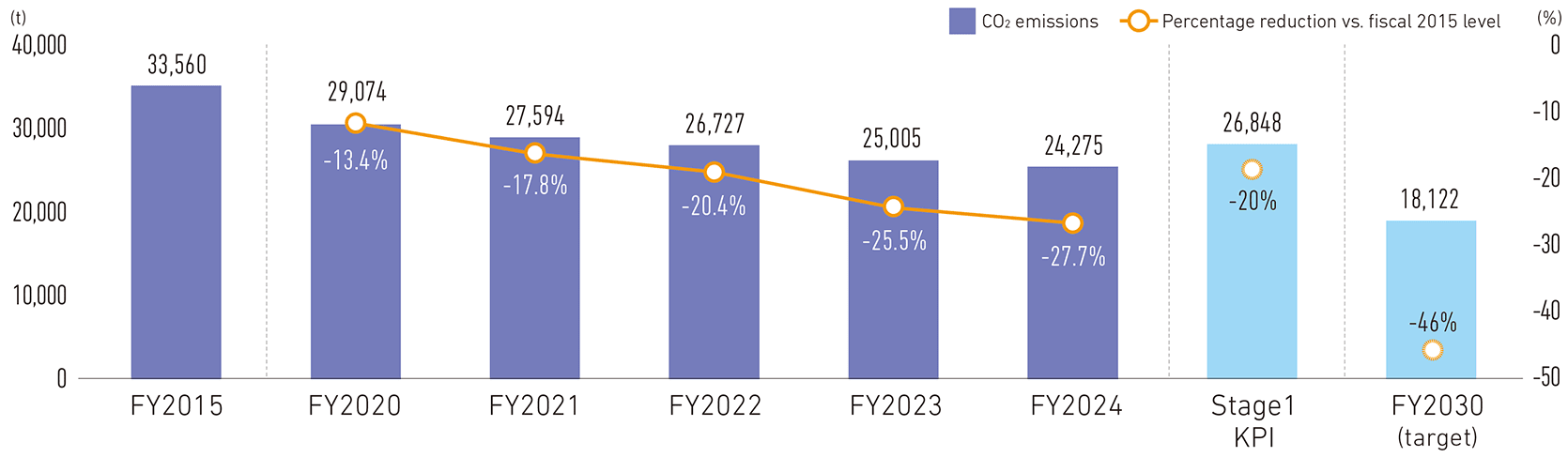
2030 target: Reduce CO2 emissions (Scope 1 + Scope 2) 46% in fiscal 2030 vs. fiscal 2015 level
CO2 emissions and percentage reduction vs. fiscal 2015 (Scope 1 + Scope 2) level
Measures toward achieving targets
Systematic upgrades and proactive capital investment in equipment
To reduce CO2 2 emissions, we are systematically upgrading antiquated manufacturing equipment, air conditioning, and other equipment to new models with superior energy conservation functions, while introducing LED lighting and other measures.
In addition, we are currently considering proactive capital investment in heat conversion and highly efficient machinery and making preparations for concrete implementation.
The Takaoka Plant uses equipment systems and machinery much more efficient than ones at previously existing manufacturing centers to reduce energy use.
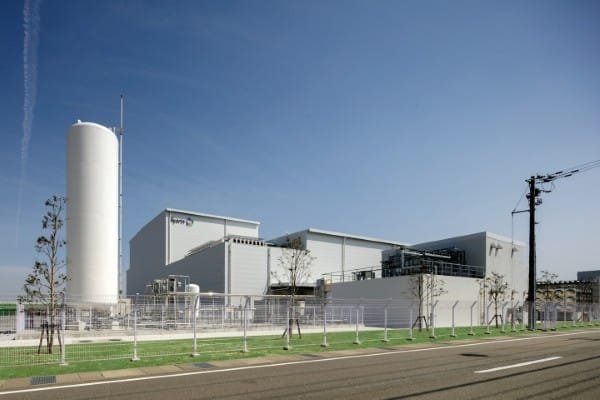

It is also using liquefied natural gas (LNG), other clean energy, and renewable energy including hydroelectric power to reduce air pollution and global warming. As a result, CO2 2 emissions in fiscal 2024 were reduced approximately 2,932 tons.
We are also working to lessen the environmental impact of wastewater and have completed installation of equipment to prevent pollution of nearby rivers and emission of odors in surrounding areas.
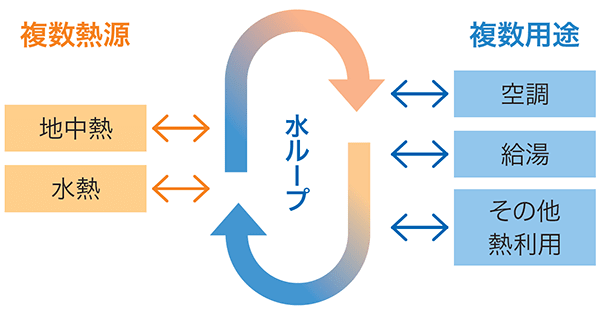
The WATARASE Research Center has installed ReHP* technology. Operation of this system during fiscal 2024 reduced electric power consumption 68,375 kWh and CO2 2 emissions approximately 29.5 tons compared with those from conventional heat pumps for air conditioning and heating, achieving energy savings of approximately 35%.
Introducing renewable energy
We are working to reduce CO2 2 emissions by gradually replacing electric power at research centers and plants with power from renewable sources. Of the electricity used during fiscal 2024, the percentages derived from renewable sources were 20% at the WATARASE Research Center, 20% at the Noshiro Plant, 100% at the Takaoka Plant, 0% at the Inami Plant, and 10% at the Shiga Plant.
Reducing number of sales force vehicles and replacing with hybrid vehicles
From the perspective of preventing global warming, we are reducing the number of sales force vehicles and replacing vehicles with ecologically friendly versions including low emission vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
As of March 2025, all 803 sales force vehicles met the standard for low emission, and of these, 316 are hybrid vehicles, which were introduced in 2004. In addition, these vehicles adhere to the Ministry of the Environment’s “Eco-Driving” guidelines regarding their impact on the environment and for traffic safety.
Other initiatives
Water resource management
In addition to monitoring the volumes of water intake and wastewater outflow, we are striving to preserve water resources by using wastewater treatment buildings and primary treatment equipment at research centers and plants for the appropriate management of the quality of water outflow.
Water intake during fiscal 2024 totaled 261 thousand m3 , and wastewater volume amounted to 107 thousand m3 , with wastewater pH, BOD, and SS at all research centers and plants within standard levels.
Air pollution management
We regularly measure and manage soot particles as well as NOx and SOx emissions from boilers and generators.
Reducing waste materials
We are proactively implementing 3R (reduce, reuse, recycle) initiatives for waste materials to effectively use limited resources.
Chemical substance management
We strive to appropriately manage specified chemical substances by following the Japanese government’s Pollutant Release and Transfer Registers (PRTR) system.
Biodiversity
Noshiro Plant participates in a citizen’s volunteer activity to protect the Kaze-no-Matsubara pine forest near the plant, to provide local residents with a place to relax.
In addition, WATARASE Research Center has installed birdhouses in trees adjacent to the WATARASE YUSUICHI wetland and confirmed the location of nests as a way to enhance the environment for wild animals in the Center’s grounds.
Kyorin Group material flow (Fiscal 2024)
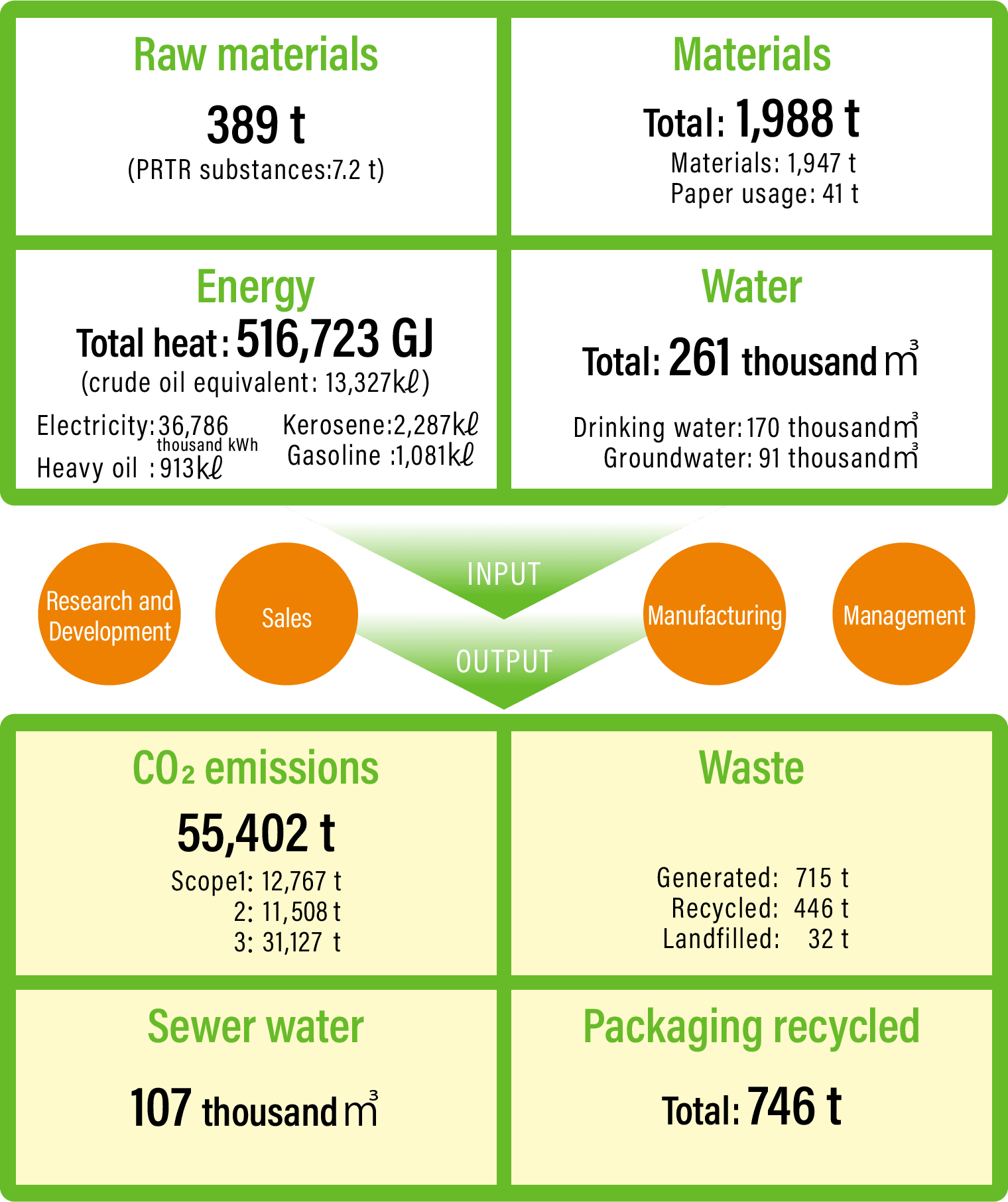
CO2 emissions (Scope 1, 2, and 3)
The Kyorin Group strives to expand the scope of coverage to calculate CO2 emissions throughout its supply chains.
- Scope 3Other indirect emissions
-
-
Purchased products and services
7,374t -
Capital goods
17,844t -
Fuel- and energy-related activities not included in Scope 1 or 2
1,796t -
Business travel
1,395t -
Employee commuting
952t
-
- Scope1Direct emissions from the use of
fuel in-house and industrial processes -
-
Direct emissions
12,767t
-
- Scope2Indirect emissions associated
with use of purchased electricity and heat -
-
Indirect emissions from energy sources
11,508t
-
- Scope 3Other indirect emissions
-
-
Waste materials from businesses
284t -
Disposal of products sold
481t
-
- Scope 3Other indirect emissions
-
-
Transport, delivery
1,001t
-


